Laravel is among the leading PHP frameworks at this time. Laravel is extensively favoured for building scalable, secure and high-performance web applications. Nevertheless, while Laravel contains a number of security features that come pre-installed within the framework, no application is free from cyber threat exploitation. Cybercriminals continue to exploit vulnerabilities such as SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and Broken Authentication in order to compromise web applications.
Protecting a Laravel application from common attack types requires a combination of using the built-in security features of the framework together with the implementation of best practices and ongoing monitoring. In this document I will highlight common security threats to a Laravel application and provide best-practice recommendations for protecting a Laravel application from Threats to security.
Why Laravel Security Is Critical
Laravel applications often handle sensitive data such as user credentials, payment information, and business-critical records. A single security breach can result in:
- Data leaks and financial loss
- Service downtime and operational disruption
- Legal and compliance penalties
- Damage to brand reputation
Security is not a one-time task—it is an ongoing process that evolves alongside your application.
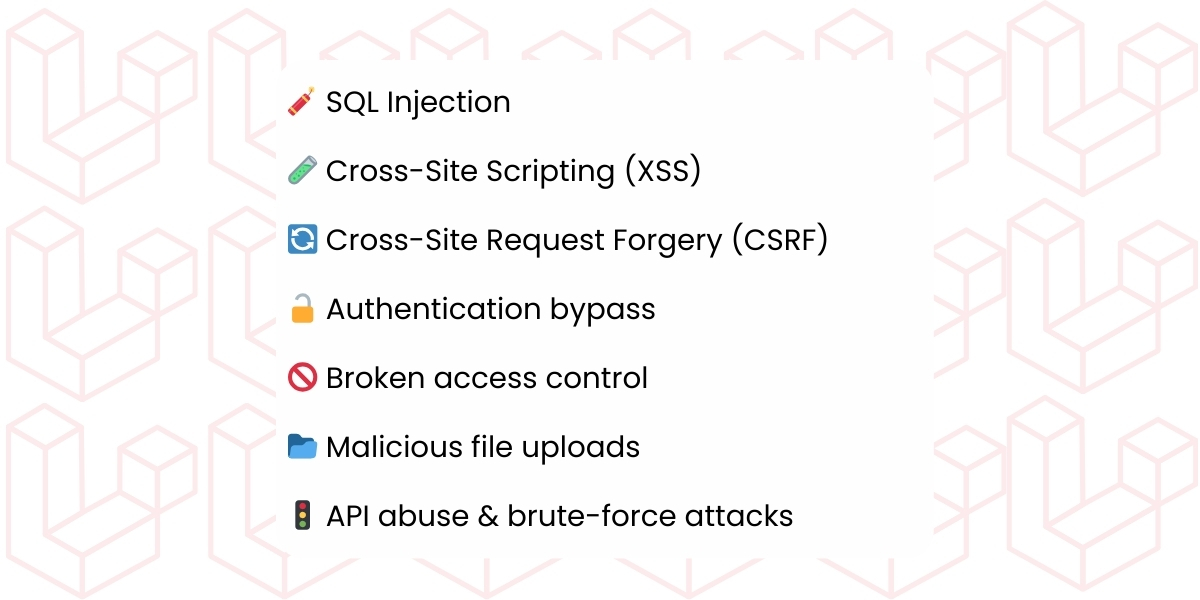
Common Attacks on Laravel Applications
When you know how common attacks are going to happen, you can help your application’s defenses and make enhancements to protect against these potential attack vectors.
SQL Injection Attacks
When an attacker enters unvalidated input into a database, they can change what is being asked to be returned with this query; thus giving them access to unauthorized data, deleting data, and/or compromising a whole database.
Laravel helps to mitigate this issue through parameter binding and query abstraction. However, if you were to not create a proper query, there could still be a chance of an attack.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS attacks allow attackers to inject malicious scripts into the web pages that other users can see. These scripts are used to steal cookies, session tokens and any sensitive data that may be stored in a user’s browser.
Any application that is displaying user generated content that has not been properly handled for output is an easy target for this kind of attack.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
CSRF attacks are when an attacker tricks a user that has been authenticated into performing an action on another user without them knowing that the action is being performed. This could involve updating a user’s account details or submitting requests without approval.
Laravel offers some protection for CSRF attacks, but the developer must properly implement it across all forms and endpoints.
Authentication/Authorization Flaws
One of the problems with weak authentication mechanisms is that an attacker may be able to log into the system by bypassing the login process or access to information that has not been authorized for them to view.
Some of the most common issues with weak authentication mechanisms are as follows:
- Weak password policies
- Poor session management
- Inadequate Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
It is essential to have good identity management to prevent account compromises.
File Upload Vulnerabilities
Unrestricted file uploads can allow attackers to upload malicious scripts or malware. If executed, these files can compromise the entire application or server.
API Abuse and Rate-Limit Attacks
APIs without proper request limits are vulnerable to brute-force attacks and denial-of-service attempts. Excessive API calls can degrade performance or expose sensitive endpoints.
How to Implement Security Best Practices in Laravel Applications
Laravel Natively Provides Security Features
Laravel provides a number of built-in security features that are present in every Laravel application, including:
- CSRF protection
- Hashing passwords
- Validating input
- Creating secure authentication scaffolding
All of these security features can be leveraged to create a strong security foundation for your application.
Sanitize and Validate User Input
All user input should be assumed to be an untrusted input.
Things you can do to minimize the risk associated with untrusted user input include:
- Using Laravel’s built-in validation system to validate all request data
- Limiting the data type and length of the data
- Not allowing any unexpected parameters in requests
All of the above protect against injection and data manipulation attacks.
Preventing SQL injection
When using Laravel’s Eloquent ORM and query builder, the Eloquent ORM and query builder automatically protect against SQL injection.
You can further strengthen security by:
- Never using raw queries unless absolutely necessary
- Always using parameter binding for database interactions
- Limiting database user permissions
Protect against XSS (cross-site scripting) attacks
When using Laravel’s templating engine, the engine automatically escapes output, thus reducing the risks associated with XSS.
Additional steps to take to protect against XSS attacks include:
- Do not output any unescaped output.
- Sanitize any user-generated content.
- Enforce strict content security policies.
Secure Authentication and Authorization
To enforce strong authentication for users, you should:
- Enforce strong password policies.
- Implement multi-factor authentication.
- Manage user sessions securely.
As for authorization, implement the following:
- Implement role-based access control.
- Always apply role-based access control to all objects.
- Only allow authorized users to perform sensitive actions.
When developing an application that supports uploading files, there are multiple ways to help mitigate the risk of file upload attacks. The following recommendations may be used to help secure uploaded files:
- Limit the types of files that can be uploaded to your application.
- Establish limits for the size of files that can be uploaded to your application.
- Store uploaded files in a secure location (e.g., outside of the web root).
- Verify uploaded files for viruses or other types of malware whenever possible.
Utilizing Rate Limiting would prevent an application from being abused, and help maintain performance.
Implementing Rate Limiting
you would:
- Reduce the number of brute-force attacks
- Prevent users from overloading your application via an API
- Help ensure that every user uses your application in a fair manner
The rate limiting of requests is beneficial in that it protects the application and preserves it’s consistency.
Secure API Endpoints
- Authentication based upon the Token
- Encrypted Communications
- Data returned in response to API calls must be limited to the minimal amount of information required.
Enable Logging and Monitoring
You should log:
- Failed Login Attempts
- Suspicious Activity
- Securely Store Logs
Ongoing Monitoring allows for the quickest possible response to incidents.
Keep Laravel and Dependencies Updated
- Update your version of Laravel and PHP
- Patching Third-Party Libraries regularly
- Remove Any Unused Packages
Keeping Your Software Up to Date is one of the best ways to defend against prolific vulnerabilities.
Security Testing and Maintenance
Security should be tested continuously.
Continuous Testing includes a variety of methods, Recommended Practices include:
- Regularly Conduct Vulnerability Assessments
- Regularly Conduct Penetration Testing
- Conduct Code Reviews for Security
- Automatically Conduct Security Tests During Your CI/CD Pipeline
By continuously testing security issues, you will ensure that you have Long-Term Protection.
Conclusion
Protecting Laravel applications from common attacks requires a combination of built-in framework features, secure development practices, and continuous monitoring. While Laravel offers strong security tools, developers must implement them correctly and stay vigilant against emerging threats.
By validating inputs, securing authentication, protecting APIs, and keeping systems updated, organizations can significantly reduce security risks and build trustworthy, resilient Laravel applications.
Investing in Laravel security today ensures safer applications, better compliance, and long-term business success.
Secure your Laravel application with proven protection strategies.
Partner with Empirical Edge to harden your code, optimize defenses, and safeguard your platform from common threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Laravel supports encryption, secure authentication, role-based access, API security, and compliance-friendly architecture, making it suitable for enterprise platforms, SaaS products, and eCommerce systems handling sensitive data.
Laravel offers secure authentication scaffolding, hashed passwords, multi-factor authentication support, API token security, and role/permission management to protect user accounts and business systems.
Laravel supports request throttling, CAPTCHA integration, IP blocking, secure API rate limiting, and firewall rules to prevent unauthorized access and bot abuse.
Empirical Edge provides Laravel security audits, attack prevention, secure architecture design, penetration testing, cloud security integration, and ongoing maintenance to keep your applications protected.