The lifecycle hooks of Vue.js are a major part of the features of the framework. The lifecycle hooks allow developers to define custom logic at certain points in the lifecycle of a Vue component. Knowing how Vue.js lifecycle hooks work is critical when developing efficient applications that can be maintained and have high-performance aspects.
The purpose of this guide is to inform how the lifecycle hooks of Vue.js provide a way for a developer to interact with their Vue components during the component’s life, what is the function of the lifecycle hooks, when to use the lifecycle hooks, and how to fully utilize the capabilities of Vue.js components.
What Are Vue.js Lifecycle Hooks?
Vue.js lifecycle hooks are methods that are called automatically by Vue at various times during the lifecycle of the component, from the moment a component is created to the point in which it is destroyed. The lifecycle hooks give developers an opportunity to access the lifecycle of the component internally, allowing them to complete tasks like data retrieval, modify the DOM, interact with the various events, clean up the component when it’s done.
Every Vue component goes through a predictable series of events, called the component lifecycle, and the lifecycle hooks give a developer access to all of these events.
Use of Lifecycle Hooks in Vue.js
Lifecycle hooks are used to control how an application performs and what it’s doing. Developers utilize lifecycle hooks to:
- Determine when logic will run during the lifecycle of a component
- Run tasks at the best possible time for optimal performance
- Control how to interact with APIs, manage timers, listen for events, etc.
- Avoid memory leaks by cleaning up properly
- Provide end-users with better experiences by rendering faster and smoother
If we didn’t have lifecycle hooks then managing the behavior of components would be much more difficult and would increase the risk of errors.
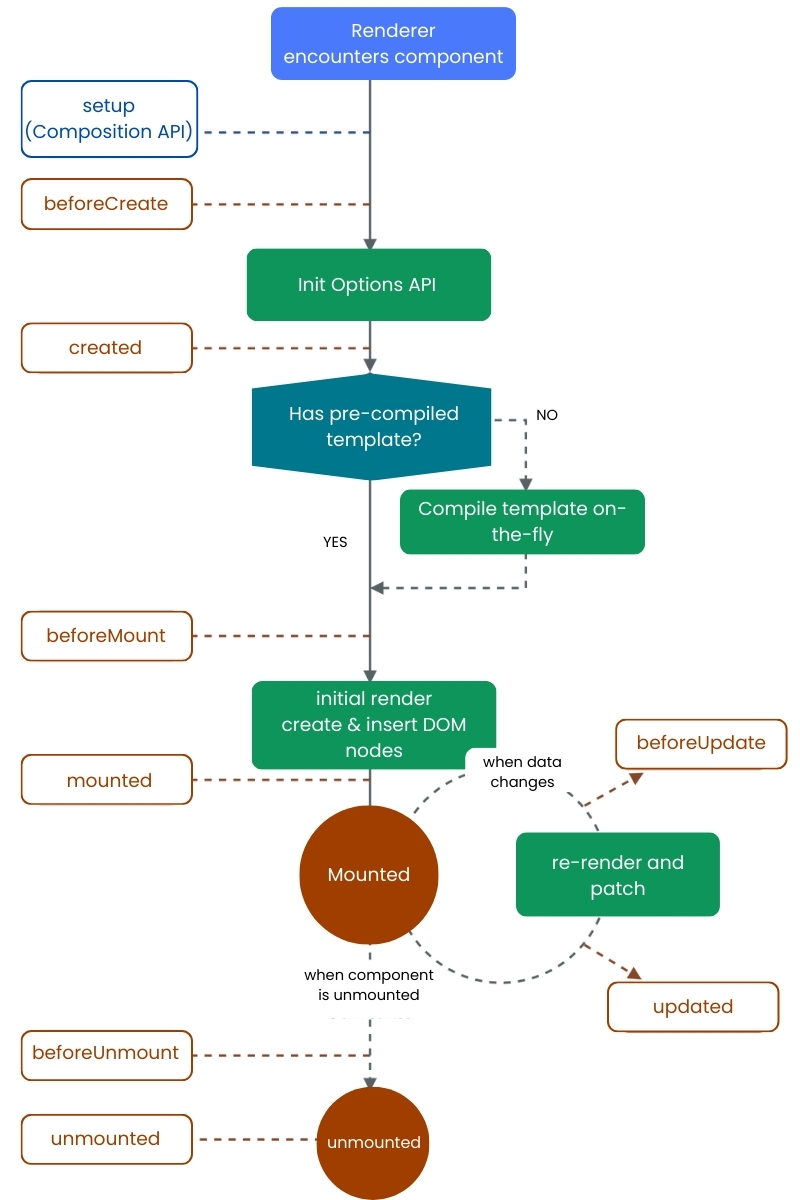
The Vue.js Component Lifecycle Overview
The lifecycle of a Vue component can be divided into four main phases:
- Creation
- Mounting
- Updating
- Unmounting
Each phase has specific lifecycle hooks that allow developers to run logic at the right moment.
Creation Phase Hooks
The creation phase is when a component is initialized but not yet rendered to the DOM.
Before Create
This hook runs immediately after the component instance is initialized. At this stage, reactive data and events are not yet available. It is rarely used in most applications.
Created
This hook runs after data observation and event setup are complete. While the DOM is still unavailable, this is an excellent place to:
- Fetch data from APIs
- Initialize variables
- Set up application logic
The created hook is commonly used because it allows access to component data before rendering.
Mounting Phase Hooks
The mounting phase begins when Vue renders the component and inserts it into the DOM.
Before Mount
This hook is called right before the initial render. The template is compiled, but the DOM has not yet been updated. It’s useful for last-minute logic before rendering.
Mounted
Once the component is fully rendered and attached to the DOM, the mounted hook is triggered. This is one of the most frequently used lifecycle hooks.
Common use cases include:
- DOM manipulation
- Initializing third-party libraries
- Accessing rendered elements
- Triggering animations
Updating Phase Hooks
The updating phase occurs when reactive data changes, causing the component to re-render.
Before Update
This hook runs when data changes but before the DOM updates. It allows developers to inspect or modify state before the UI reflects the changes.
Updated
This hook runs after the DOM has been updated in response to data changes. It’s useful for:
- Responding to UI updates
- Running logic that depends on updated DOM elements
- However, excessive logic here can affect performance, so it should be used carefully.
Unmounting Phase Hooks
The unmounting phase occurs when a component is removed from the DOM.
Before Unmount
This hook runs right before a component is destroyed. It’s ideal for cleanup tasks such as:
- Clearing timers
- Removing event listeners
- Cancelling network requests
- Unmounted
After the component is completely removed from the DOM, this hook is triggered. At this stage, all component bindings are destroyed.
Proper use of unmounting hooks is essential to avoid memory leaks and performance issues.
Examples of Using Lifecycle Hooks
Lifecycle hooks allow developers to accomplish many of the things they need to do when developing applications in a real-world setting such as:
- Fetching data when a component is first being rendered
- Controlling how the user interacts with the UI after it has been rendered
- Updating content dynamically based on how users interact with it
- Cleaning up resources when components are removed
- Safely integrating external libraries throughout your application.
When choosing which hook to use developers can ensure performance is smooth and the behavior of their applications is predictable.
Best Practices for Using Vue.js Lifecycle Hooks
To make the most of using Vue.js’s lifecycle hooks here are some best practices to follow:
- Utilize created when you want to fetch data or initialize data
- Use mounted only when you need access to the DOM.
- Avoid performing heavy logic inside of updated.
- Always clean up any resources created in before Unmount.
- Make sure to keep lifecycle hooks concise and narrowly focused.
- Where possible, use reusable logic and composition with your lifecycle hooks.
A well-designed structure for lifecycle logic makes for better readability, maintainability, and also debugging ease.
Modern Vue 3 Development Using Lifecycle Hooks
Lifecycle hooks are a critical part of Vue 3, which has enhanced the performance and adaptability of the framework. Developers are now able to manage the lifecycle of a Component more effectively, especially when creating scalable and enterprise-level applications.
The importance of understanding lifecycle hooks is even greater in the development of a modern application, as it helps in improving the way complex state is managed and allows developers to create performance-sensitive applications.
Conclusion
Vue Js life cycle hooks, providing developers with tremendous flexibility and power to control their Component behavior throughout the life of the Component. Understanding how and when to use these hooks will enable developers to build faster, cleaner and more robust applications.
Lifecycle hooks are an essential tool in Vue Js development when working on data retrievals, DOM manipulation and resource cleanup.
Frequently Asked Questions
Developers can load data only when needed, delay heavy operations, optimize rendering, and remove unused listeners or timers—resulting in faster, more efficient Vue.js applications.
Yes. Lifecycle hooks are commonly used to connect APIs, load dashboards, update live data, and manage WebSocket or real-time services in business applications.
Yes. Lifecycle hooks make application flow predictable, allowing developers to debug faster, isolate performance issues, and maintain code more efficiently over time.
Empirical Edge builds high-performance Vue.js applications using best practices, lifecycle optimization, API integrations, and scalable architectures to deliver secure and business-ready solutions.