In the current era of the web, users expect web apps to have a fast response time and also update dynamically—without needing to reload the page over and over again. Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) makes this possible by performing seamless communication between the client and the server in the background. Ajax is one of the foundational technologies of the interactive, real-time web applications of today.
This article describes what Ajax is, how it works, and why it is an important tool for building responsive web applications.
What is Ajax?
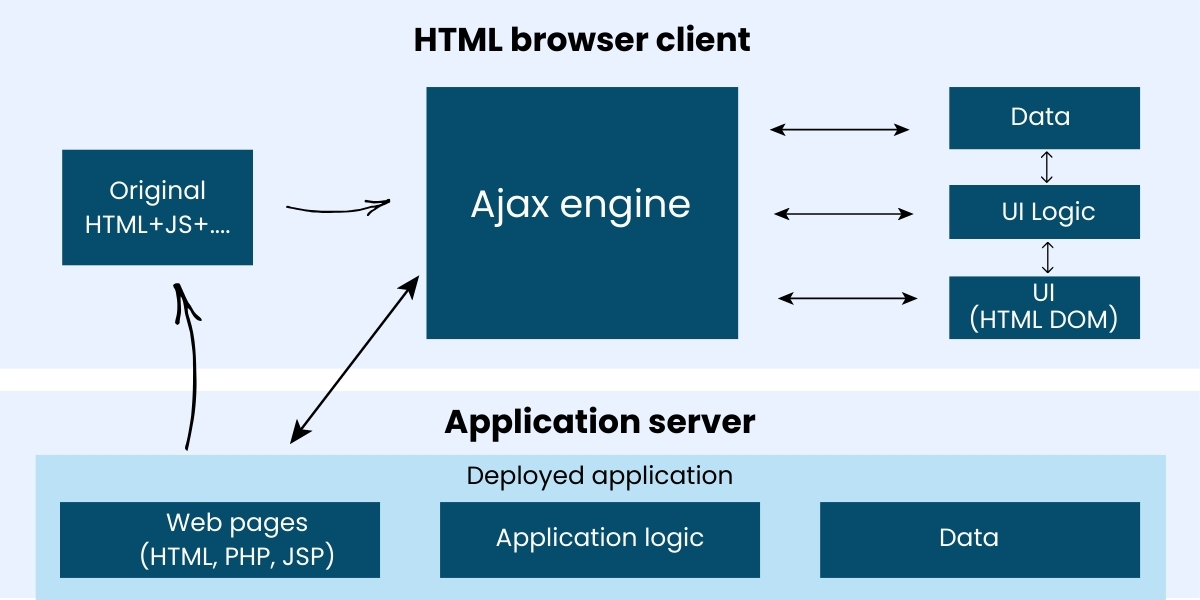
Ajax is an acronym for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML, though modern implementations may use JSON instead of XML. Ajax is not a programming language itself, but a technique to enable web pages to request and send information to the server asynchronously, so the page does not need to reload when new data is needed.
In other words, Ajax lets a web page asynchronously update part of its content without requiring the whole page to reload. This will yield a more what users expect in terms of performance and more user-friendly experience overall.
Example where Ajax is used:
- Live search suggestion on Google
- Social media notification auto-refresh
- Form submissions without page reload
- Real-time chat and messaging apps
How Ajax Works
Ajax works by using a combination of web technologies to exchange data asynchronously. Here is a full breakdown of the process:
User Action:
A user activates an action – for example, clicks a button, or selects an item from a dropdown.
JavaScript Creates a Request:
The browser uses JavaScript (often but not always through the already familiar XMLHttpRequest object, or more recently fetch() API) to make a request to the server
Server Processes the Request:
The server takes the request, processing it (possibly pulling the information from a database) and sends it back to the browser with a response – typically returning it in JSON format, or XML format.
Browser Receives the Response:
The response is handled by JavaScript – the entire page does not reload.
Dynamic Page Update:
Only a portion of content on the page is updated with new data while it appears quickly and feels interactive.
Key Components of Ajax
To have a full understanding of Ajax, it is important to understand the main components:
- HTML / CSS = Structures and styles a website page.
- JavaScript = Controls the logic, User interaction, and Ajax request.
- XMLHttpRequest / Fetch API = Manages asynchronous transmission of data back and forth from client to server.
- Server-Side Script (PHP, Node.js, Python, etc.) = Process the request and returns with a response.
Advantages of Utilizing Ajax
Improved User Experience:
Reduce reload times, and increase responsiveness by only updating sections of a web page.
Reduced Server Load:
Decrease bandwidth usage by only sending necessary data.
Asynchronous Communication:
Users can interact with the page while waiting on a data fetch.
Improved Performance:
Applications feel faster and more responsive, improving user experience as a whole.
Real-Time Interactions:
Ajax can power real-time experiences, live notifications, chat, or instant form validation.
Common Ajax Use Cases
- Live Search Suggestions: Updates search results in real time as the user types.
- Validation of Forms: Validates user input in real time before submission.
- Feeds that Auto-Refresh: Posts, comments, notifications, etc.
- Infinite Scrolling: Data loads while a user scrolls down.
- Dashboards with Data: Charts or metrics that are fetched and updated in real time.
Challenges and Best Practices
While Ajax has many advantages, it is not without the following challenges:
Challenges:
- Difficult debugging in situations with multiple asynchronous requests.
- Potential security risk (including APIs being exposed or leaked data).
- Problems with search engines not indexing a site properly.
Best Practices:
- Make sure you handle errors properly when an ajax request fails.
- Do some protection on your endpoints to prevent unauthorized access.
- Reduce the response data as much as possible to improve performance.
- Think about fallbacks for browsers that have JavaScript disabled.
Conclusion
Ajax changed the way web applications communicate with servers, making any website faster, smoother, and more interactive. If you learn how Ajax works and follow best practices, developers can create that user experience that feel seamless and responsive, which is a modern web design expectation.
It doesn’t matter if you are requesting data from an api, validating a form submission, or creating a real-time dashboard, if you want to be an efficient front-end developer, you must learn Ajax.
Build Dynamic Web Experiences — Master AJAX for Responsive, Fast Interfaces
Frequently Asked Questions
AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) lets web applications communicate with the server behind the scenes without reloading the entire web page, enabling dynamic content updates and smoother user experiences.
Yes — although traditional XML-based approaches are less common, the AJAX concept remains central to modern asynchronous communication (using JSON, Fetch API, Axios, etc.) for dynamic interfaces.
Common AJAX uses include handling live form submissions without refresh, fetching search suggestions, updating UI elements in real-time, and loading content dynamically.
No — although AJAX originally referenced XML, most implementations today use JSON for data transfer due to its simplicity and efficiency.