The foundation underlying a truly successful, efficient, and scalable database is a principle known as “data normalization.” Data normalization is a principle that applies to any database, whether you are building a single application or managing an entire corporation; by normalizing data, professional developers are able to maintain the stability, organization, and performance of their database. Unfortunately, many developers have either not heard of normalization or have failed to understand what it means for their database when they normalize it, resulting in extensive amounts of unnecessary work maintaining their database, duplicate data, and highly inefficient queries.
In this blog post, We are going to be discussing what exactly is data normalization and why it is important, the effects of data normalization on the performance of an application long-term and, most importantly, some of the best practices that should be followed by all database developers.
What is Data Normalization?
Data normalization refers to a method where a relational database is designed in such a way that the same data does not exist in multiple locations. A DBMS is designed to provide certainty and predictability in storing data; therefore, normalization is very much about the way that you structure and configure your database. By using normalization in your database, you can:
- Reduce duplicate data
- Set data elements in their appropriate location
- Maximize efficiency and performance of a database
- Make it easier to support and maintain a database
- Prevent commonly experienced anomalies when updating, deleting, and inserting data.
Normalization follows a specific set of rules (also referred to as Normal Forms) for structuring and organizing a database, starting with the first (1NF) and moving to more complex Normal Forms, such as BCNF, 4NF, and 5NF. The higher the Normal Form you achieve, the more predictable and structured your database is.
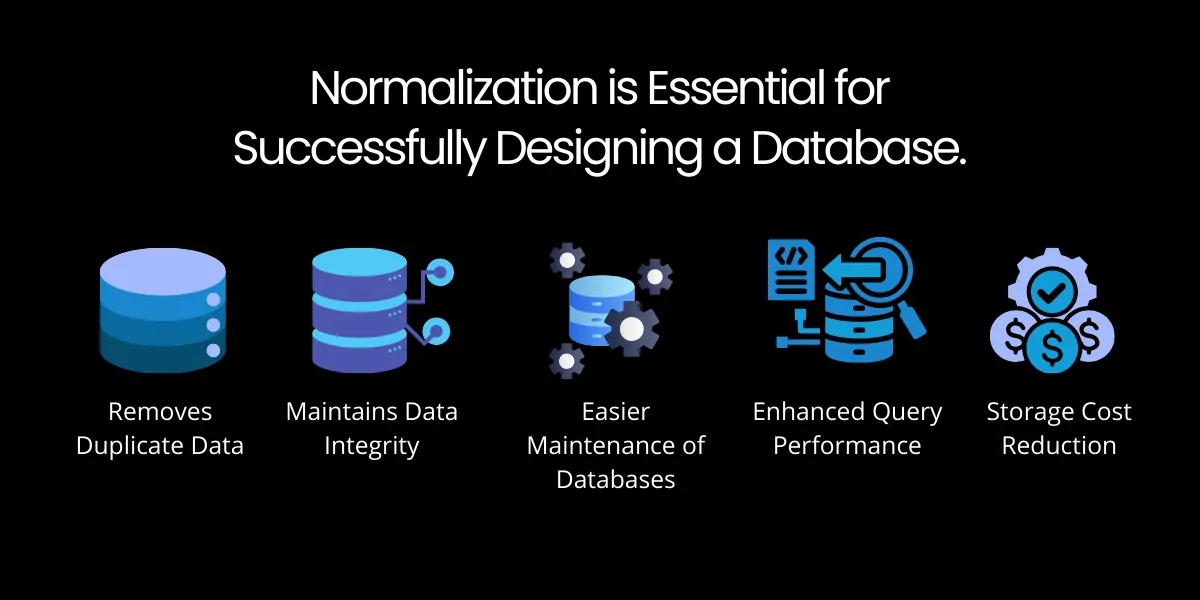
Normalization is Essential for Successfully Designing a Database
1. Removes Duplicate Data
Duplicate data is the most significant contributor to inefficient databases because duplicate data will take up space, slow down query performance, and complicate the updating process. By using normalization, all the information in your database will be stored only once, which will minimize wasted space and maximize the amount of usable space in your database.
As an example, if you were to store your customer information in multiple locations (tables), a potential mismatch could occur with your customer records. The use of normalization ensures that the customer information is only stored in one centralized place.
2. Maintains Data Integrity
Data Integrity means that the data stored in your database remains true, consistent and reliable through all of the tables. Without normalization, there is the likelihood of potential mismatches and errors occurring with your data, especially when many tables rely on data shared by other tables (in a large application).
With the use of normalization, we can ensure:
- proper and accurate relationships
- consistent sets of values
- up-to-date data from all tables
- fewer errors when data is changed
Applications such eCommerce, banking, healthcare, and ERP systems depend heavily on maintaining accurate and reliable databases. Therefore, it is critical to maintain a single source of truth for all data.
3. Easier Maintenance of Databases
Databases are evolving and growing, as are the applications that are building upon or supporting those databases. Over time, as databases become more complicated in their structure, the maintenance of those databases becomes more cumbersome.
Normalization provides a cleaner, easier way to maintain:
- Database updates
- changes in Database schema
- Table modifications
- The ability to scale and re-design effectively
Because of Normalization, a Developer or Administrator can quickly and accurately make changes to a database without compromising the quality and reliability of the stored data or the relational integrity of the Database.
4. Enhanced Query Performance
The normalization of a database results in smaller, more structured tables. Therefore, when a database engine executes queries against these tables, they can be processed more quickly because less duplicate data and fewer large tables must be searched.
While denormalized data can be advantageous for analytical purposes, normalized databases are ideal for transactional application performance (OLTP). Examples of these types of applications include:
- CRM
- Inventory
- Authentication
- Ticket/Booking
5. Storage Cost Reduction
Despite the prevalence of modern cloud-based storage, optimized data is still important. Redundant data significantly increases backup, restore, and replication times, and thus increases overall storage costs.
Through normalization, you can eliminate unnecessary data so that:
- Your backup needs are reduced.
- Your data restoration process will be faster.
- You’ll have better disaster recovery ability.
- You’ll save money, particularly if you have many installations in use across multiple locations.
The result of these benefits is that all databases hosted in the cloud will benefit from increased storage space and improved performance through better index performance.
The Three Primary Anomalies That Normalization Solves
Normalizing a database prevents three common types of anomalies:
Update Anomalies in Databases
The need to change the same value in multiple places creates the opportunity for the value to be incorrect at one location or the other.
Anomalies in Inserting
Inserting data cannot occur without additional unrelated information that must be inserted simultaneously with it.
Anomalies in Deleting
Accidentally removing an important associated record.
The structure provided by normalization solves all of these problems by organizing data into logical, clearly defined database tables with defined associations.
The following is a brief overview of the normal forms
Normalization does not require that you memorize all the normal forms to understand the concept. Here’s a quick breakdown of what normal forms are:
- The first normal form (1NF) eliminates repetitive/duplicate data and ensures that each field only contains a single value. A field containing atomic values is an atomic value.
- The second normal form (2NF) satisfies 1NF and eliminates partial dependencies on primary keys.
- The third normal form (3NF) satisfies 2NF and eliminates transitive dependencies. The Boyce-Codd normal form (BCNF) and higher normal forms are used when working with more complex relationships, where there may not be a clear logical relationship between each attribute. Most modern database designs are either in 3NF or BCNF because they provide the best combination of throughput and efficiency.
Examples of the benefits of normalized database designs are
- E-commerce systems that provide a consistent data format for product, customer, and order data.
- Banking and financial systems which reduce the number of errors made during transactions, account maintenance, and auditing.
- Health care systems that ensure patient records, diagnoses, and medications are all accurately recorded and maintained in a timely manner.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms that allow users to create a single source of truth (STT) for all records for all time while allowing the resulting data to scale and be easy to manage, and
- Enterprise-level applications that provide long-term scalability, reporting consistency, and system reliability. Normalized database designs offer benefits in all types of industries working with structured data.
The conclusion
Utilizing data normalization is not simply a way to design a database; it is an investment in the long-term stability, ability to perform well, and reliability of your application. By removing duplicates, increasing the integrity of your data, and simplifying the maintenance of your systems, normalizing your data will allow for an efficient and sustainable system as your business grows.
Data normalization is important when developing both small applications and large enterprise-level applications in order to maximize the effectiveness of those applications. Developers, database administrators, and organizations that manage high volumes of structured data should all accept and use normalized data to create high-performing systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Normalization is specifically designed to eliminate duplicate records and prevent update anomalies, ensuring your business works with clean, reliable, and up-to-date information.
Key benefits include improved data accuracy, easier maintenance, better scalability, reduced storage costs, enhanced security control, and reliable analytics for business intelligence.
Absolutely. As databases grow, unnormalized data leads to performance issues and reporting errors. Normalization ensures enterprise systems remain scalable, structured, and easy to integrate.
While normalized databases may have more tables, they are actually easier to manage, update, and secure. They reduce long-term complexity by keeping data organized and eliminating inconsistencies.
Empirical Edge designs and optimizes normalized database architectures, cleans existing data, restructures legacy systems, and ensures your databases are scalable, secure, and analytics-ready.