To create applications that run on Windows not only requires the writer to compose working code, it also requires the writer to test, and debug the code to achieve reliable, stable and performance. An application that is well-tested and debugged gives your users a better overall experience, reduces the frequency of issues after release, and can save time in the long-term, maintenance of the application. This article examines best practices, tools, and techniques to test and debug Windows applications.
1. Value of Testing and Debugging
Testing, and debugging, is a valuable step of the software development lifecycle. Testing determines whether or not the application responds and behaves as expected, while debugging allows the developers to find, and eliminate errors or inconsistencies in their code. Together, testing, and debugging, enhance the quality of the software, reduce the level of errors, and ultimately enhance the experience of the end-users of the application.
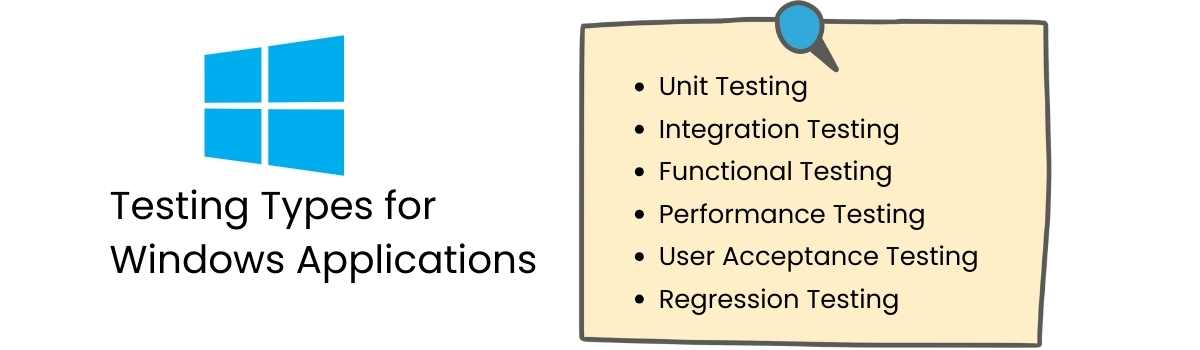
2. Testing Types for Windows Applications
Different types of testing will ensure that the application is completely reliable:
- Unit Testing – Testing the application focuses on testing an individual function or component for correctness.
- Integration Testing – Tests the interaction of the different modules properly combines.
- Functional Testing – Tests the application’s result in context of the business requirements, and the expected application behaviors.
- Performance – Tests the responsiveness, stability, and resource usage under load.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) – Confirms that the application to be put into release satisfies the requirements of the end-users.
- Regression Testing – Validating that the new change or changes or updates do not break the existing functionality of the application.
3. Tools for Testing Windows Applications
There are a variety of great testing tools available to Windows developers that can make testing easier:
- Visual Studio Test Explorer – Built-in unit testing for .NET applications.
- NUnit or xUnit – Popular frameworks for writing and automating unit tests.
- Appium and WinAppDriver – Good for automating user interface (UI) testing for desktop applications.
- Postman – Good for testing Application Programming Interface (API) integration with hybrid Windows applications.
- Microsoft Test Manager (MTM) – Tool for managing test plans, using test suites, and creating reports on execution or event logs.
Automation can significantly reduce repetitive work and ensure consistent testing across builds.
4. Debugging Efficiently
Debugging is identifying the root cause of bugs and unintended behaviors. In order to debug efficiently you need a combination of the right tools and smart thinking:
- Use the Visual Studio Debugger – Set breakpoints, inspect variables, and see the behavior of code at runtime.
- Use IntelliTrace – Review past data on debugging events to trace the issue without having to reproduce the issue.
- Analyze Logs and Exceptions – Use structured logging, such as Serilog or NLog, to find issues faster.
- Remote Debugging – Debug code that runs on another machine or environment, such as Azure.
- Memory and Performance Profiling – Diagnose problems with memory leaks, performance bottlenecks, or CPU usage using diagnostic tools.
5. Implementing Continuous Testing and Integration
By including automated testing in a CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipeline, developers can ensure that each code change passes through a set of tests before being deployed. Using platforms such as Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, or Jenkins, developers can build, test, and deploy Windows applications with limited human interaction.
This ongoing process supports reducing the effects of human error, increasing the speed of development, and assuring the application quality remains consistent.
6. Best Practices for Testing and Debugging
To obtain usable and effective results, developers should consider these best practices:
- Clear and comprehensive test cases should be written.
- Testing should occur early and often inside the development cycle.
- Testing scenarios that will repeat should be automated.
- Every issue discovered should be logged and documented for re-use later.
- Version control should be used to manage changes and aid in the debugging process.
- Testing should be done in conditions similar to ‘real-world’ applications for monitoring performance.
Conclusion
Proper testing and debugging are essential in the delivery of reliable and user-friendly Windows applications. By using the right tools, automation and structured methods within the process of testing and debugging will detect issues early, enhance performance, and provide high-quality software. Ultimately, the rigorous testing and debugging practices lead to increased customer loyalty and overall success of your Windows apps.
Frequently Asked Questions
Testing ensures a Windows app behaves as expected and debugging identifies and fixes issues early, improving reliability and user experience.
Key test types include unit testing, integration testing, functional testing, performance testing, user acceptance testing (UAT), and regression testing.
Common tools include Visual Studio Test Explorer, NUnit/xUnit for automated tests, Appium/WinAppDriver for UI automation, and Postman for API testing.
Use tools like the Visual Studio Debugger with breakpoints and variable inspection, IntelliTrace for historical debugging, and structured logs to quickly pinpoint errors.