As applications create immense amounts of data, processing and analyzing that data in an efficient manner is becoming increasingly important. The Aggregation Framework from MongoDB provides a means of aggregating data from many sources into a single dataset. It was created to allow users to effectively summarize, analyze and interpret large amounts of data using the aggregation framework. All developers need to be familiar with the aggregation framework as it is one of the key tools used within a NoSQL (Not Only SQL) database.
Whether you are developing analytic dashboards, analyzing user data, developing real time reporting solutions or anything else, the MongoDB Aggregation Framework will provide unparalleled speed and flexibility in creating these solutions. This article discusses what the aggregation framework is, how it operates, why it is important and also gives best practices for using it.
What is MongoDB’s Aggregation Framework?
The MongoDB Aggregation Framework is an incredibly powerful tool that allows you to take your stored data records and turn them into computed results. The Aggregation Framework operates in a manner similar to SQL’s GROUP BY, JOIN and many analytic functions. However, it provides much greater degrees of flexibility and scalability for working with unstructured and semi-structured data.
Aggregation provides several capabilities including:
- Filtering and transforming user data
- Grouping user documents
- Computing summary values based on a document(s)
- Joining user documents across various collections
- Sorting and reshaping user documents
- Performing advanced analytics on user documents
Aggregation uses a pipeline-based architecture, whereby the data flows through a number of different stages, and as the data passes through each stage it is transformed. This modular design allows for highly efficient processing of large amounts of user data.
Why the Aggregation Framework Matters
In today’s data-driven world, applications often need to perform complex operations such as:
- Calculating sales reports
- Analyzing user behavior
- Generating performance metrics
- Filtering real-time events
- Producing insights for dashboards
The Aggregation Framework simplifies these operations by processing data directly on the server, reducing the amount of data transferred to the application. This results in faster performance, cleaner code, and improved scalability.
How Does MongoDB’s Aggregation Pipeline Work?
The aggregation pipeline is the primary method MongoDB uses to process data. The aggregation pipeline is composed of multiple stages. Each stage is responsible for a particular operation. The results produced by each stage will become the input for the next stage. Therefore, the data will flow through each stage in the pipeline.
A couple of common aggregation stages are:
$match
The $match aggregation stage can be used to filter documents based on certain criteria. Filtering data before the data has passed through all of the stages improves performance.
$group
The $group aggregation stage allows developers to group documents by key and then to apply various operations: count, sum, average, etc.
$project
The $project aggregation stage allows developers to “shape” the output that will be created by the aggregation operation. Developers can “shape” the output by specifying whether to include fields, exclude fields, or transform fields.
$sort
The $sort aggregation stage sorts the list of documents based on field(s). The order can be either ascending or descending.
$limit and $skip
Developers can use the $limit and $skip aggregation stages to control pagination and the size of results returned from an aggregation operation.
$lookup
The $lookup aggregation stage performs a left outer join against another collection. This allows time to combine documents from multiple collections without flattening the schema.
$unwind
$unwind will allow developers to deconstruct array(s) into separate documents. This capability is often useful when performing analytical operations on an array field.
Each stage of the aggregation pipeline allows developers to create more complex pipelines to return to a user, from simple report creation to complex analytic workflows.
Key Benefits of the MongoDB Aggregation Framework
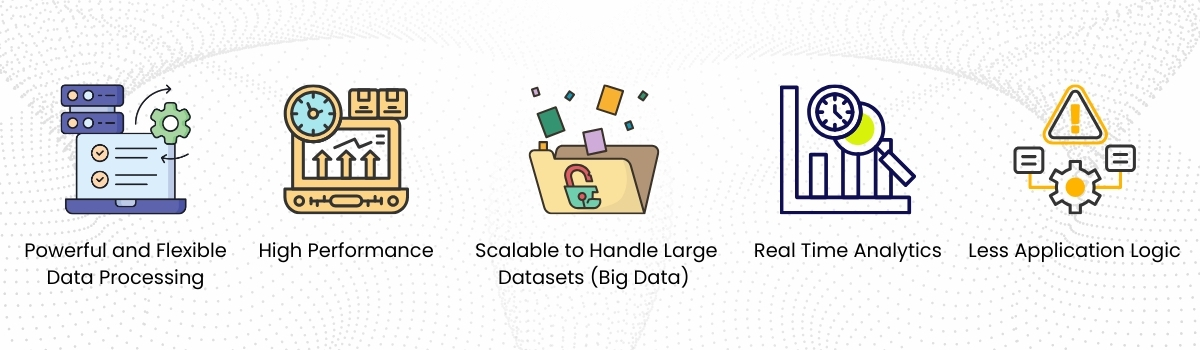
MongoDB Aggregation Framework-Here are the Key Benefits of the Aggregation Framework:
1. Powerful and Flexible Data Processing
Unlike SQL, which relies on a rigid schema for all data, MongoDB operates using JSON-like documents giving it the ultimate level of flexibility for the transformations that can be applied on nested fields.
2. High Performance
The MongoDB aggregation framework processes all the stages of pipelines at the database level reducing latency and improving performance. Many stages of operation are processed with indexes and an in-memory optimization technique making it well suited for working with huge datasets.
3. Scalable to Handle Large Datasets (Big Data)
The Aggregation Framework is designed to work with sharded clusters that enable the spreading of resource-intensive processing operations across multiple servers, thus allowing businesses to perform complicated analytical operations on large amounts of data.
4. Real Time Analytics
MongoDB allows you to perform real-time analytical operations using efficient data processing and is able to power dashboards, logs, reporting, live monitoring and analytics systems without needing an external system to perform the analyses.
5. Less Application Logic
Since MongoDB is where data transformation happens, your application code is cleaner and easier to maintain. This results in faster processing times and greater maintainability than if the transformation were done by an external application.
Most Frequent Uses of the Aggregation Framework
1. Business Intelligence and Reporting
Examples of summarized reports include:
- Total Sales
- Monthly Revenue
- Customer Statistics
- Product Performance Indexes
2. Real-Time Analytics
Examples Include:
- Dashboard Monitoring
- Tracking of User Activity
- Fraud Detection
The aggregation pipeline provides insights quicker than other methods.
3. Data Transformation
When Client Applications receive cleaned, reshaped, or enriched data from the Aggregation Pipeline before being sent to those applications.
4. Log/Event Processing
Log/event histograms are ideal for monitoring logs, detecting patterns of errors and tracking the activity of your system.
5. Data Integration Via $lookup
Create a relational-like view without moving the data to a relational database.
MongoDB Aggregation Framework Compared to Map-Reduce
Before the creation of the aggregation pipeline, MongoDB utilized the Map-Reduce framework as the primary means of performing advanced data analysis. While Map-Reduce provides the user with an extensive number of options, Map-Reduce’s customizability comes at the cost of speed.
Advantages of Using the Aggregation Framework Include
- Faster Data Processing
- Simplicity of Syntax
- Increased Scalability of the Aggregation Framework
- Built-In Optimization
Most of the MongoDB Applications built in recent years rely primarily on the Aggregation framework.
Conclusion
The aggregation framework of MongoDB is one of the most robust tools used for data processing in new generation applications because it can perform a wide range of operations from filtering and grouping to analytical and real-time reporting. The aggregation framework provides developers with the ability to derive useful information from their data all in a fast and efficient manner.
Due to its pipeline-oriented architecture, its various performance optimizations, and its many customizable features, the aggregation framework is a critical component for all systems designed for use with MongoDB. Mastering the aggregation framework will greatly enhance your application’s ability, whether building dashboards for big data or performing transformations of documents in real time.
Frequently Asked Questions
MongoDB aggregation offers faster processing for large, unstructured, and semi-structured datasets. It enables real-time analytics, flexible data modeling, and complex transformations without moving data to external tools, making it ideal for modern, scalable applications.
Yes. MongoDB aggregation is designed to work with large-scale datasets and supports indexing, sharding, and distributed processing, making it suitable for high-traffic and enterprise-level applications.
Empirical Edge designs, optimizes, and manages MongoDB aggregation pipelines for reporting systems, real-time analytics platforms, SaaS products, and enterprise applications to ensure performance, scalability, and accuracy.