APIs are the foundation upon which all modern web & mobile applications are built. APIs facilitate convergence in the way that systems communicate with each other (system-to-system), how services provide data to clients (service-to-client), and how customers interact with those services (client-to-service).
PHP APIs drive the majority of e-commerce platforms, financial applications, Software as a Service applications, and enterprise applications. As the number of APIs continues to rise, so too does the risk of being attacked on APIs—malicious attackers now see unsecured APIs as a prime target for their attacks based on things such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and Denial of Service attacks.
It is vitally important that PHP API developers implement security measures. Any business or organization building an application with sensitive personal information must ensure that they have secured their PHP API before they even launch it to the public. This article outlines best practices, typical threats, and some tried and true methods for securing APIs built with PHP.
Importance of Ensuring Security for PHP APIs
PHP APIs often contain valuable business information, such as user passwords, bank account balances, and company secrets, and even one exploited vulnerability can open up your whole network.
Unsecured PHP APIs may cause:
- Data access without proper authorization
- Deleted or modified data
- Account hacked
- Damage to the organization due to non-compliance
- Loss of customers and revenue.
Using secure API security practices will provide multiple layers to reduce the attack surface, while also ensuring the reliability and safety of inter-system communication through a secure, trusted channel.
Common Security Threats to PHP APIs
Understanding potential risks is the first step toward building secure APIs.
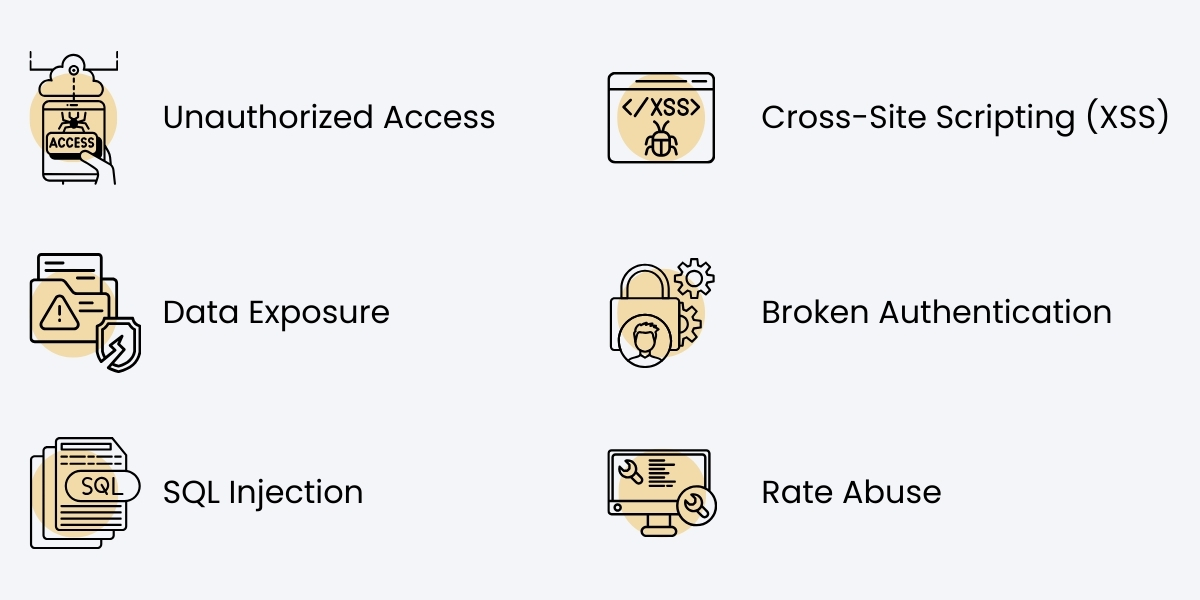
Unauthorized Access
Attackers may exploit weak authentication mechanisms to access protected endpoints.
SQL Injection
Improper handling of user input can allow attackers to manipulate database queries.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Malicious scripts injected through API inputs can compromise connected applications.
Broken Authentication
Poor session handling or token management can expose user accounts.
Data Exposure
Returning excessive or sensitive data in API responses increases risk.
Rate Abuse
Without rate limiting, APIs are vulnerable to brute-force and denial-of-service attacks.
Best Practices for Securing Your PHP APIs
Ensure You Have Robust Authentication Options
Authentication only allows authorized users / systems access to your API.
Common Authentication Options Include:
- Token-Based Authentication (JWT)
- OAuth 2.0 for Third-Party Applications
- API Keys for Specific Purpose Access.
Tokens Must be:
- Securely Created
- Stored Safely
- Rotated Frequently
Establish Role-Based Authorization Process
Authentication verifies a user’s identity while authorization determines what that user can do.
Make Sure:
- Users Access Only Those Endpoints Applicable to Their Assigned Role
- Privileged Users Are Given Only Those Endpoints With Access to Sensitive Operations
- End User Permissions / Rules Associated With User Accounts are Enforced To All Endpoints
Creating Fine Tune Access Control Reduces Exposure of your API to Compromised Access Type A User May Have To Access the API.
Provide HTTPS Access to All PHP APIs
Every PHP API Needs To Be Configured To Use HTTPS To Provide Encryption of Data During Transmission.
Benefits Include:
- Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
- Secure Transmission of User Credentials and Tokens
- Support For Trust and Compliance
API Requests Should Always Be Accepted Via Secure HTTPS Connection.
Validate and Sanitize All Input Data That Comes Into Your API
User Input Is An Easy Target For Attackers; Therefore, Input Data Needs To Be Validated and Sanitized.
Recommended Best Practice Options Include:
- Utilizing Strict Data Types
- Limiting Length of Input
- Rejecting Unusual Parameters
- Escaping Output As Necessary
Validation and Sanitizing Input Data Will Help Reduce the Chance of Injection Attacks Being Successful.
Safeguard Against SQL Injection
Database Access is essential to All PHP APIs.
Utilize:
- Prepared Statements
- Parameterized Queries
- ORM Frameworks That Were Developed With Sql Injection Protection In Mind.
Implement a Throttling and Rate Limiting Process
Rate limiting works by regulating the maximum number of requests that can be processed per user or per IP address.
Examples of Benefits
- Brute-force attacks are prevented
- Server resources are protected
- Stability of APIs is increased
To maximize performance and usage, all users will be treated equally.
Implement Security with API Responses
It is important to limit exposure of information to the API by not returning additional fields in requests.
Best Practices
- Return only those fields that are actually needed
- Mask sensitive information.
- Use the appropriate HTTP status code for the request
- Do not return verbose error messages in production
By returning minimal information, there is less opportunity for information leakage.
Implement Security when Handling Errors and Logging
The more detailed an error message is, the easier it is for an attacker to identify a vulnerability.
Perform the Following:
- Return generic error messages to clients
- Store detailed logs in a safe location for internal use
- Do not include any sensitive information in the logs.
This provides a balance between security and usability.
Implement Versioning for APIs
Versioning will ensure long-term security and maintainability of the API.
Advantages:
- Securely deprecate older endpoints
- Prevent any breaking changes
- Permit gradual security enhancements
Compatibility for clients with older versions of the API.
Establish Monitoring and Audit Procedures
Monitoring continuously helps identify any questionable activities.
Essential Procedures:
- Record patterns of API usage
- Monitor any processing of failed authentication attempts.
- Regularly audit access logs.
By identifying questionable activities early, the damage caused by an attack is minimized.
Data Protection and Compliance
Depending on the business sector you are in, you may be required to adhere to specifications such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR for PHP APIs.
Security to Companies should help by including:
- Access logs
- Data Encryption
- Secure Backups
- Regularly Auditing
Not only does compliance protect your users, but it also prevents the company from being liable for penalties.
Conclusion
Protecting a PHP API is a necessary step toward protecting Data, System Integrity, and Long-term success for Your Business. Implementing strong authentication and authorization, input validation and encryption as well as monitoring the activity of your API all help to greatly reduce the risk to your API.
APIs are powering the digital transformation, investing in strong security measures will be a good business decision not just a technology decision. Following the best practices and strategies for securing PHP APIs will keep PHP APIs and their ability to scale, perform and securely work in the ever-increasingly connected world.
Protect your PHP APIs from threats.
Empirical Edge offers expert API security solutions, from authentication hardening to vulnerability mitigation — built for your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. When built with proper security architecture, encrypted data handling, secure authentication, and continuous monitoring, PHP APIs can safely power enterprise platforms, SaaS products, and eCommerce systems.
Absolutely. Existing PHP APIs can be reviewed through security audits, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and code refactoring to eliminate risks without rebuilding the API.
PHP APIs should be continuously monitored and formally tested during development, before deployment, and regularly after updates to ensure long-term protection.
Empirical Edge provides PHP API security audits, secure architecture design, authentication implementation, penetration testing, performance-safe protection, and ongoing monitoring to ensure safe and scalable API systems.