The implementation of AJAX transformed the development of Web-based applications by allowing the asynchronous loading of data, updating of dynamically generated content on an ongoing basis for users, and creating a smoother user experience overall when interfacing with these types of applications. However, since AJAX allows developers to load content asynchronously during the course of running an application, developers face unique challenges when testing/deploying/debugging these types of applications. Some of the main issues associated with AJAX applications include delayed responses, hidden failures, network-related issues, and UI inconsistencies that occur without the implementation of test/debug practices.
This document provides guidance on the most effective methods associated with testing/debugging AJAX applications to allow for continued support and enhancement of application performance in varied environments.
Understanding Common AJAX Issues
Before diving into tools and techniques, it’s important to understand the typical problems developers face with AJAX applications:
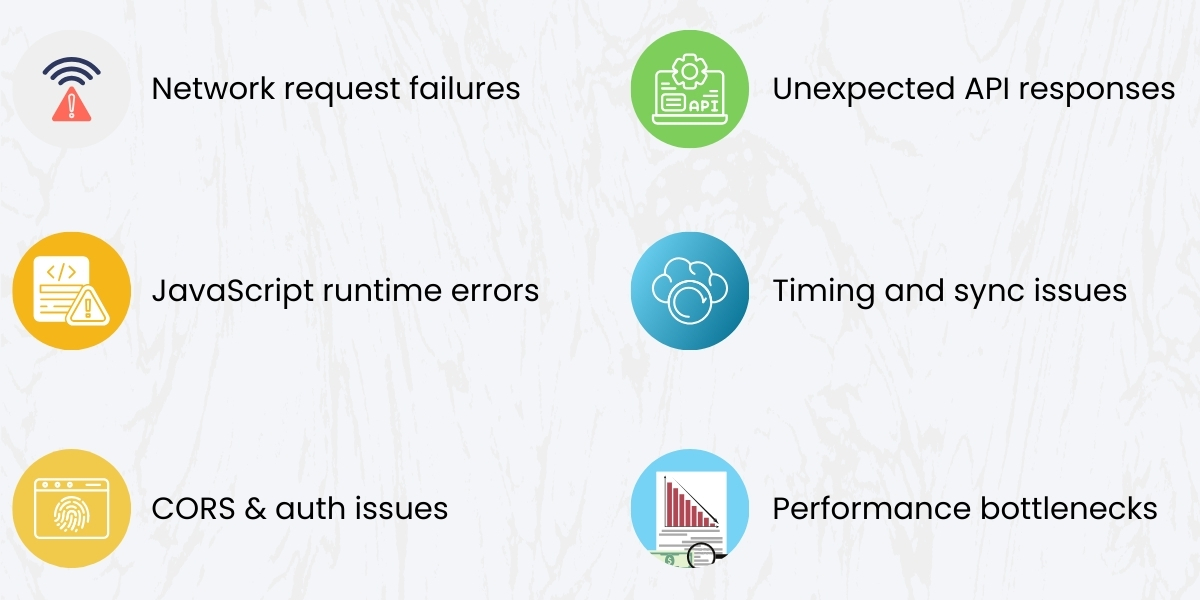
- Network request failures
- Unexpected API responses
- JavaScript runtime errors
- Timing and synchronization issues
- CORS and authentication problems
- Performance bottlenecks
- Inconsistent behavior across browsers
Identifying these early helps reduce troubleshooting time and improves overall application quality.
Effective Debugging of AJAX Applications
1. Utilize Your Browser’s Developer Tools
Developer tools available with modern web browsers enable you to effectively debug AJAX applications.
Features of Developer Tools:
- View the request and response information using the browser’s network tab
- Use the browser’s console to view JavaScript errors
- Identify server-side problems using HTTP status codes
- View the response payload for each request to verify data integrity
By viewing network activity, developers can have a clear picture of the path between the client and the server, as well as the exact way each request and response is processed.
2. Log Errors and Events Clearly
When debugging an asynchronous workflow, meaningful logging helps a developer easily identify issues.
Best Practices for Logging:
- Log the request start and end times
- Log error messages in context
- Log unexpected API responses
- Log all retry attempts/failure
When logs are clearly defined, it makes identifying the underlying cause much easier.
3. Handle Errors Gracefully
AJAX errors that aren’t caught can be very disruptive to application functionality.
When building an AJAX application, ensure your application:
- Can handle network timeouts
- Detects server errors
- Has a user-friendly message to inform users of errors
- Can fall back to a safe state
By implementing error-handling practices that promote graceful handling of unexpected failures, a developer can improve both debugging effectiveness as well as the user experience.
4. Create Realistic Test Scenarios
Trying to debug an application only in ideal conditions can provide misleading results.
Scenarios to simulate during testing include:
- Slow, unstable network connectivity
- Partial failures on the API
- Large response sizes
- Unauthorized or expired sessions
By replicating these test scenarios in your development environment, you can identify debugging challenges that may arise during production.
Recommended Approaches to Testing AJAX Applications
A structured approach needs to be implemented for testing AJAX applications, which require coverage on different levels of functionality.
1. Async Logic Unit Testing
Unit tests for AJAX applications are used to verify that the individual components behave as expected. The focus should be on:
- How a request is initiated
- How a response is handled
- What errors/exceptions can occur and how they are handled
- Whether conditional rendering is being done correctly based on the returned API data
Using mocks for the API responses allows for testing various scenarios without having to rely on live servers.
2. API Integration Testing
API integration testing allows the front-end and back-end of an application to work together properly.
The primary focus should be on:
- What format the request is in when sending to the API
- How the API authenticates requests
- Whether the returned data from the API is consistent.
- How the response is handled by the front-end and back-end.
API integration tests often catch problems not caught by unit tests alone.
3. E2E Testing
E2E (End-to-End) testing allows you to test how users will interact with an AJAX application from start to finish.
Examples of E2E test scenarios include:
- When a user submits a form with an AJAX request
- When a user updates their Profile Page
- When a user navigates through the website without having to reload the page.
- When a user receives an error and allows them to retry.
E2E tests ensure that asynchronous behaviors function seamlessly from the users’ perspective.
4. Performance Testing AJAX Requests
With AJAX requests, performance problems are generally unnoticed until a high volume of user traffic is present.
Performance testing allows you to:
- Identify performance issues by measuring the amount of time taken to receive a response from the server.
- Identify which API endpoints are slow.
- Identify which requests are redundant or made more than necessary.
- Identify which requests can be optimized by reducing their size.
Improved performance of AJAX requests results in reducing server load and allowing the end user to have an improved user experience.
Compatibility Across All Web Browsers, Operating Systems, and Devices
AJAX behavior may behave differently depending upon what browser(s) are being used to access the application.
As such, thorough testing should consist of:
- Using different types of web browsers and versions, i.e. Internet Explorer, Chrome, Firefox, etc.
- Testing on both Mobile Devices and Desktops/Laptops
- Testing across various screen sizes
- Testing across Touch and Keyboard
If you perform the above steps, AJAX application will behave more consistently when used in a real-world setting.
AJAX Application Security Testing
As AJAX applications typically make external requests for data using API’s, it is essential that you perform a security test for the following areas of such applications:
- Validate all user input
- Authenticate and Authorize users
- Prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Securely store sensitive information
- Prevent unauthorized access to your API’s
By performing thorough security tests on your AJAX applications, you are protecting the users of your application and your application’s integrity.
Automating AJAX Testing to Save Time and Money
When you have a complex AJAX application, there will come a time when manual testing is not sufficient. Automating the testing of AJAX applications will provide you with the following benefits:
- Faster regression testing
- Consistent Test Coverage
- Detect Errors Early
- Reduce Human Error
Automated tests should be added to your CI/CD pipeline, to ensure you consistently deliver quality software during development.
Best Practices for Effective Testing and Debugging AJAX Applications
To maintain a high-quality AJAX application, the following best practices should be followed:
- Write clear, maintainable Asynchronous Logic
- Document all API Contracts
- Avoid sending Unnecessary and/or Duplicate Requests
- Implement Consistent Error-Handling Patterns
- Continuously Monitor Logs and Performance
- Test Early, Test Often
By following the above practices, you will reduce the number of bugs that you find, improve the long-term maintainability of your application and create a better experience for users of your application.
Conclusion
Debugging and testing AJAX applications is essential for delivering fast, reliable, and user-friendly web experiences. By leveraging browser tools, implementing robust testing strategies, simulating real-world scenarios, and automating tests where possible, developers can confidently manage asynchronous behavior and minimize production issues.
With a structured approach, AJAX applications become easier to maintain, more secure, and better equipped to scale as business needs grow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Debugging identifies inefficient scripts, excessive requests, and performance bottlenecks, helping optimize response times, reduce server load, and improve overall application speed.
Absolutely. Existing systems can be audited, debugged, performance-tested, and optimized without rebuilding the application.
Empirical Edge provides AJAX performance audits, functional and security testing, error debugging, automation testing, and ongoing support to ensure stable, fast, and scalable web applications.